SEARCH
Everything You Need to Know About Aspirin
If you’ve ever reached for a pain reliever, chances are you grabbed an aspirin. It’s cheap, easy to find, and works on headaches, fevers, and minor aches. But there’s more to this little tablet than just "pain‑killer." Below we break down the most useful facts so you can take aspirin safely and get the best results.
How Aspirin Works and When It Helps
Aspirin belongs to a class called NSAIDs (non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs). It blocks an enzyme that creates prostaglandins – chemicals that cause pain, fever, and inflammation. Because of this, aspirin can:
- Lower a mild to moderate headache or toothache.
- Reduce fever when you’re feeling hot.
- Ease muscle soreness after a light workout.
Doctors also prescribe low‑dose aspirin (usually 81 mg) for heart health. The tiny dose thins the blood just enough to prevent clots, which can lower the risk of a heart attack or stroke in high‑risk patients.
Dosage Basics and Safety Tips
For most adults, the standard over‑the‑counter dose is 325 mg to 650 mg every four to six hours. Don’t exceed 4 g (four thousand milligrams) in a day – that’s the upper limit for safe use.
When you’re taking low‑dose aspirin for heart protection, stick to the doctor’s prescription. It’s usually taken once daily with food or a glass of water to avoid stomach upset.
Watch out for these common pitfalls:
- Stomach issues: Aspirin can irritate the lining of your gut. If you have ulcers, gastritis, or a history of bleeding, talk to a pharmacist before using it.
- Kids and teens: Never give aspirin to anyone under 18 with a viral infection – it’s linked to Reye’s syndrome, a rare but serious condition.
- Mixing meds: Blood thinners (like warfarin), other NSAIDs, or certain antidepressants can increase bleeding risk. Check with your doctor if you’re on any of these.
If you miss a dose of low‑dose aspirin, just take it as soon as you remember – unless it’s almost time for the next one. In that case, skip the missed pill and continue with your regular schedule.
Aspirin Alternatives and When to Choose Them
Sometimes aspirin isn’t the right fit. Here are a few options:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Good for pain or fever without irritating the stomach, but it doesn’t thin blood.
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): Another NSAID that works similarly to aspirin but may be gentler on the gut for some people.
- Prescription antiplatelet drugs: If you need heart protection but can’t tolerate aspirin, doctors might recommend clopidogrel or similar meds.
Always discuss alternatives with a healthcare professional to make sure they match your health profile.
Latest News and Research Highlights
Recent studies suggest that low‑dose aspirin may not benefit everyone over 70 years old for primary prevention of heart disease. The guidance is shifting toward personalized risk assessment rather than blanket recommendations.
Researchers are also exploring aspirin’s role in cancer prevention, especially colorectal cancer. Early results look promising but more data is needed before doctors change practice.
Stay updated by checking reputable health sites or asking your pharmacist during routine visits. Knowledge helps you avoid unnecessary risks and get the most out of a simple tablet.
Quick Takeaway Checklist
- Use 325‑650 mg for pain/fever, max 4 g per day.
- Take low‑dose (81 mg) daily only if a doctor recommends it.
- Avoid aspirin in kids with viral illnesses.
- Watch for stomach upset and drug interactions.
- Consider acetaminophen or ibuprofen as alternatives when needed.
That’s the core of what you need to know about aspirin. Use it wisely, stay informed, and don’t hesitate to ask a healthcare professional if something feels off. Your health is worth that extra minute of attention.

Tylenol vs. Common Pain Relievers: How Acetaminophen Stacks Up
A clear, side‑by‑side comparison of Tylenol (acetaminophen) with ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, and natural alternatives, covering safety, cost, and best‑use scenarios.
Continue reading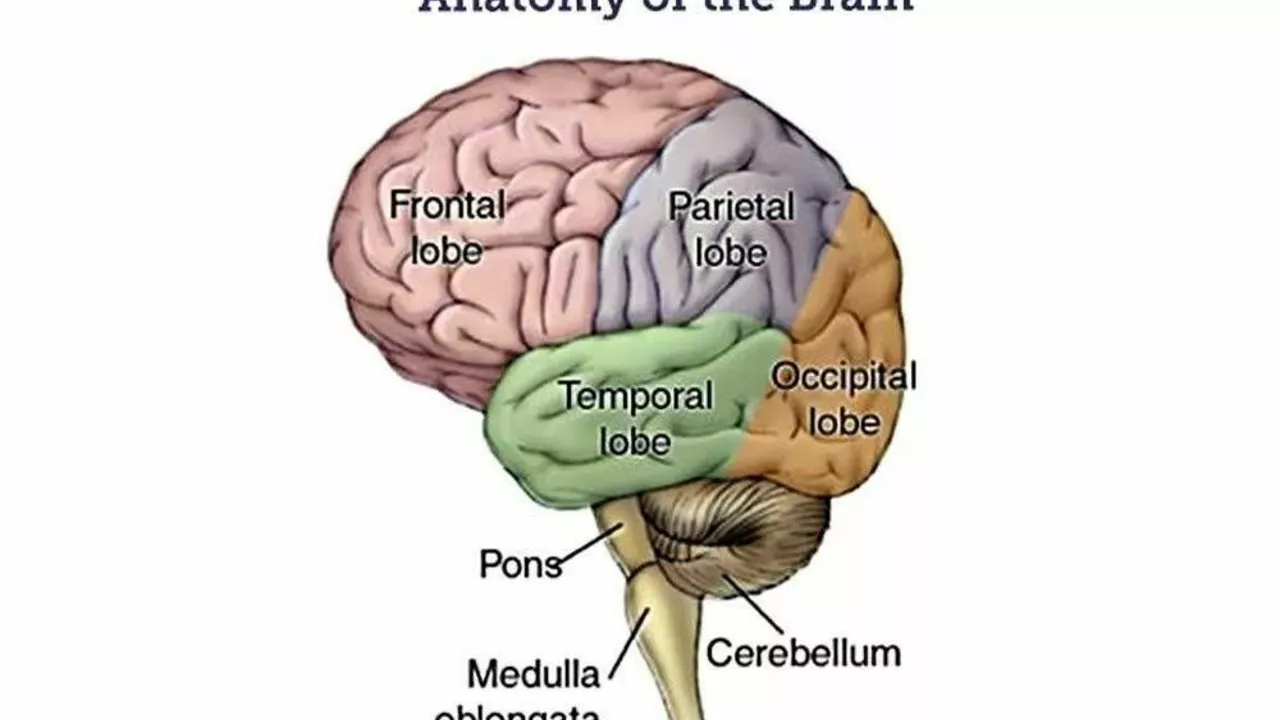
The potential benefits of aspirin for pons health and function
In my recent deep dive into health topics, I've stumbled upon some fascinating insights about the potential benefits of aspirin for pons health and function. The pons, a part of our brain, plays a crucial role in several vital functions like sleep and sensory analysis. Research suggests that aspirin, commonly used as a pain reliever, may help maintain the health of this critical brain structure and enhance its function. It's thought that aspirin's anti-inflammatory properties can protect the pons from damage and disease. However, while these findings are promising, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication regimen.
Continue reading