SEARCH
Levonorgestrel Explained – Your Quick Guide
If you’ve heard the term levonorgestrel but aren’t sure what it really means, you’re in the right spot. It’s a hormone‑based pill most people recognize as the “morning‑after” option, but it also shows up in regular birth control pills. Below we break down how it works, when to take it, where to buy it safely, and what side effects to watch for.
How Levonorgestrel Works
Levonorgestrel is a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. In emergency contraception it stops or delays ovulation so sperm can’t meet an egg. If fertilization has already happened, the pill makes the uterine lining less friendly for implantation. The effect isn’t an abortion; it simply prevents pregnancy from forming in the first place.
Buying Levonorgestrel Safely Online
Finding a reliable source online is easier than you think. Look for pharmacies that require a prescription or at least ask for basic health information. Check for a clear physical address, a valid pharmacy license number, and secure https connections. Avoid sites that promise “no prescription needed” without any verification – they’re often counterfeit.
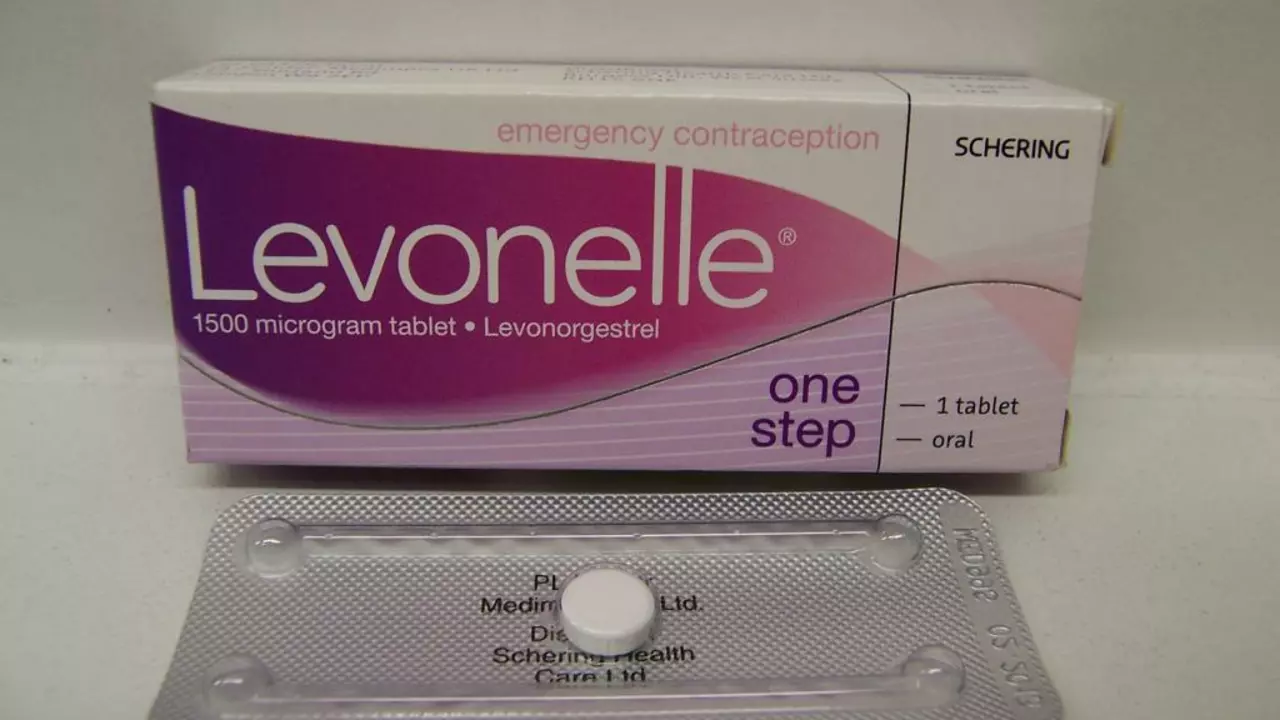
When you order, compare prices but don’t pick the cheapest option if it looks sketchy. Reputable online pharmacies usually list the generic name (levonorgestrel) alongside brand names like Plan B One‑Step or Next Choice®. Read customer reviews for shipping speed and packaging quality; a good pharmacy will ship in discreet, tamper‑evident packaging.
Once your package arrives, inspect the pills for any discoloration or broken tablets. If anything looks off, contact the pharmacy right away and keep the product for reference. Most legitimate sellers have easy return policies for faulty medication.
When to Take It and How Much
The magic window for levonorgestrel is within 72 hours after unprotected sex, but it’s most effective the sooner you take it. The standard dose is a single 1.5 mg tablet or two 0.75 mg tablets taken six hours apart. If you’re using a regular birth‑control pill that contains levonorgestrel, follow your doctor’s dosing schedule instead.
Don’t rely on the morning‑after pill as a regular contraceptive method – it’s not designed for daily use and can cause hormone spikes. For ongoing protection, consider a combined oral contraceptive or an IUD, which may also contain levonorgestrel for long‑term release.
Possible Side Effects
Most people experience mild side effects: nausea, fatigue, headache, or light spotting. These usually fade in a day or two. If you vomit within two hours of taking the pill, call your pharmacy – you may need a repeat dose. Severe allergic reactions are rare but include rash, swelling, or trouble breathing; seek medical help immediately if they occur.
Women who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain hormonal disorders should avoid levonorgestrel without consulting a healthcare professional. The pill does not protect against sexually transmitted infections, so use condoms for that extra layer of safety.
Quick FAQ
Can I take levonorgestrel if I’m on other meds? Some antibiotics and seizure medicines can reduce its effectiveness. Talk to a pharmacist before you buy.
Is it safe for teenagers? Yes, the FDA approves it for anyone 12 and older. Parental guidance is recommended but not required.
Do I need a prescription? In many countries you can buy it over‑the‑counter, but reputable online pharmacies often ask for basic health info to confirm eligibility.
Understanding levonorgestrel helps you make informed choices when you need emergency contraception or want a reliable birth‑control option. Keep this guide handy, know where to shop safely online, and always follow the dosing instructions for the best results.
The Impact of Levonorgestrel on Sleep Quality
In my recent research, I've delved into the effects of Levonorgestrel on sleep quality. Interestingly, this hormone, often used in contraceptives, may influence our sleep patterns. Some studies suggest it can lead to sleep disturbances or insomnia, while others report no significant impact. The individual's body chemistry seems to play a significant role in how this hormone affects sleep. Hence, it underscores the importance of personalized medicine and understanding how different substances can affect our sleep.
Continue reading